Site Management
Permalink Settings
The Permalinks Settings screen allows you to customize how the URLs (web addresses) for your content are structured. Creating user-friendly, descriptive permalinks helps visitors understand what a page contains before clicking, improves your site's search engine optimization, and creates a more professional appearance for your ministry website. Here you can choose from common permalink structures or create a custom format using available tags. The right permalink structure makes your content more accessible and helps people find your church's message more easily online.
Last updated on 14 Sept, 2025
By default, WordPress uses web addresses that include the date and post name. However, you can customize how these URLs are structured for your permalinks and archives. Creating a custom structure improves how your links look, makes them more user-friendly, and ensures they'll work well in the future.
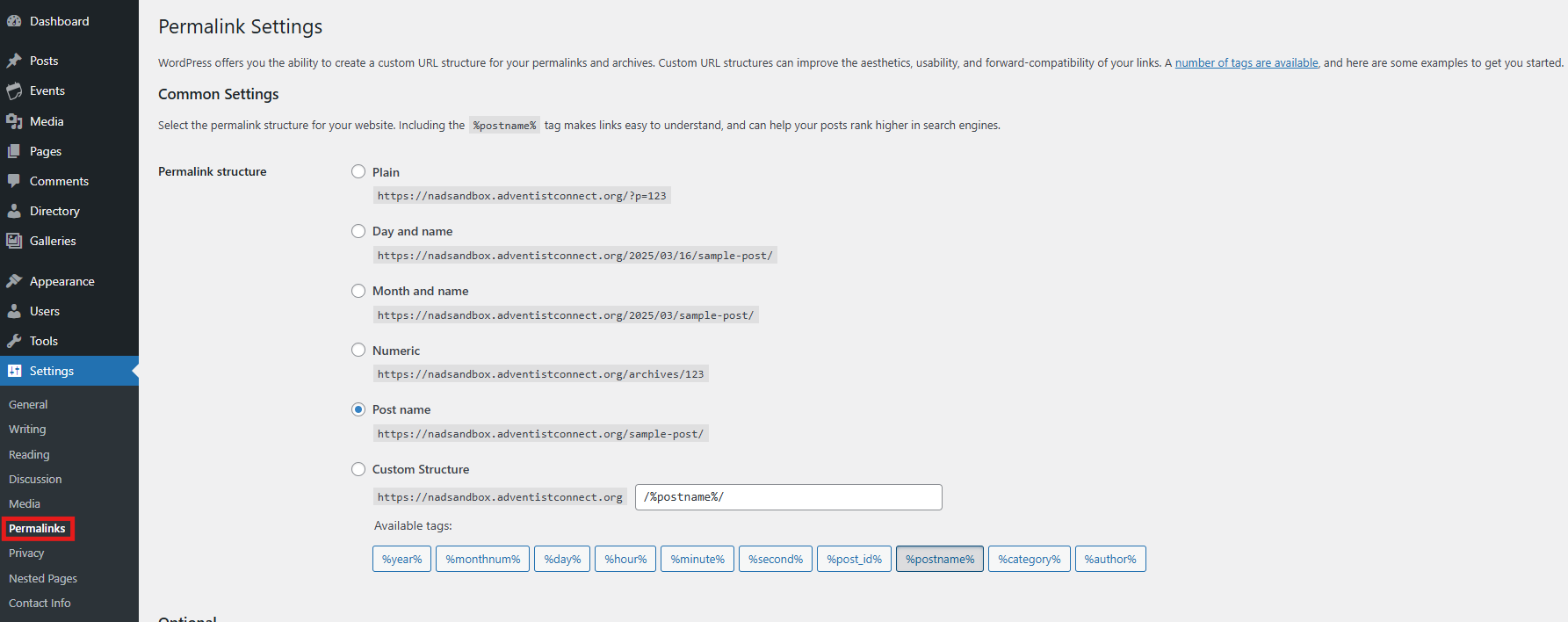
Customize Permalink Structure
Several permalink tags are available to help you create URLs that work best for your site.
Common Settings
Choose from these standard permalink structures by selecting the appropriate radio button:
Plain – Simple URLs like http://www.sample.com/?p=123
Day and name – Includes date and post name: http://www.sample.com/2008/03/31/sample-post/
Month and name – Includes month and post name: http://www.sample.com/2008/03/sample-post/
Numeric – Uses post number: http://www.sample.com/archives/123
Post name – Uses just the post title: http://www.sample.com/sample-post
Custom structure – Create your own format using available tags. For example: /archives/%year%/%monthnum%/%day%/%postname%/
Optional Settings
Customize how category and tag URLs appear:
Category base – Add a prefix for category URLs (like /topics/ to create links such as http://example.org/topics/uncategorized/)
Tag base – Add a prefix for your tag URLs
Save Changes
Click the Save Changes button to update your permalink structure. After saving, one of two things will happen:
If your .htaccess file is writeable, you'll see "Permalink structure updated" and everything is set up automatically.
If your .htaccess file is not writeable, you'll need to manually update it with the code WordPress provides in the text box at the bottom of the screen.
Remember that visiting the Permalinks screen automatically refreshes your rewrite rules, even without saving changes.
